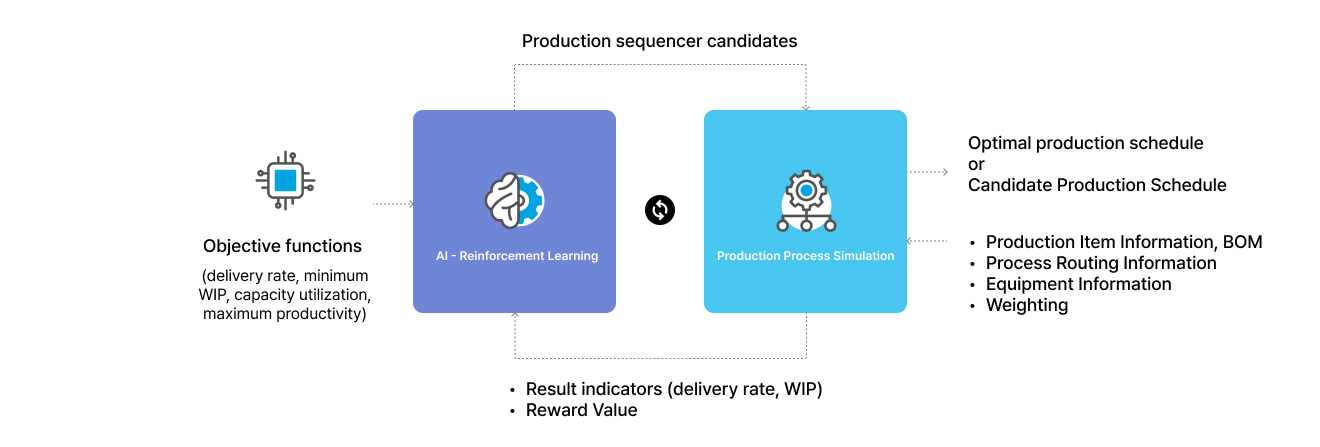
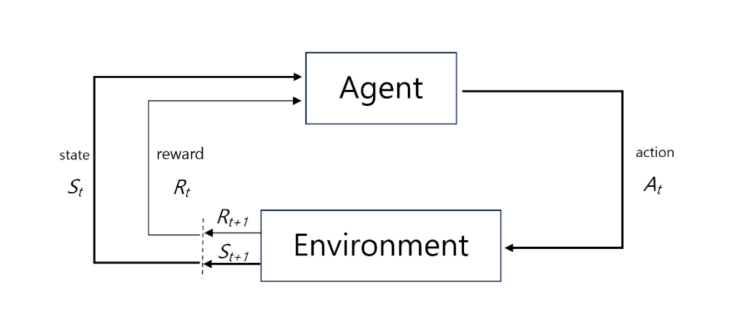
What is Reinforcement Learning?
- In the context of behavioral psychology, reinforcement entails an increase in the occurrence of a desirable behavior over time. Reinforcement learning is an application of this to computer learning.
- Agents, or self-learning computers, learn by directly interacting with their environment. The agent learns "optimal behavior patterns-policies" through trial and error, without any prior knowledge or empirical data about the environment.
Reinforcement Learning Applications
-
Robotics
In the field of robotics, reinforcement learning is applied to learn the optimal behavioral policy for a robot to move and achieve its goals in a given environment. The robot gains experience by interacting with its environment, and based on this, it learns behaviors that maximize its reward.
Example: OpenAI's 'Dactyl' is a robotic hand with reinforcement learning. Through trial and error, it learned how to skillfully manipulate objects with its fingers, optimizing its behavior to achieve a given goal. -
Autonomous driving
In the field of autonomous driving, reinforcement learning contributes to driving safety, efficiency, and traffic flow optimization. In the future, it is expected to be utilized in the development of safer and more intelligent self-driving systems.
Example: Waymo, a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc(Google's parent company), uses reinforcement learning in its self-driving cars. These vehicles learn to navigate complex traffic scenarios, adapt to different driving conditions, and improve overall driving safety. -
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Reinforcement learning is applied in the field of natural language processing to tasks such as machine translation, question answering, conversational agents, text generation, summarization, and entity name recognition by considering state, behavior, and reward. It enables models to learn optimal behavior for a given task, improving their performance in understanding and generating natural language.
Example: OpenAI's GPT-3 utilizes reinforcement learning for language understanding and generation. It performs well on tasks such as text completion, translation, question answering, and natural language dialog. -
Resource management
Reinforcement learning is used to optimize resource allocation and scheduling in a variety of industries. This includes energy management in smart grids, supply chain logistics optimization, and efficient utilization of resources in manufacturing processes.
Example: Google's DeepMind has applied reinforcement learning to optimize energy consumption in data centers. The model learns to control cooling systems and allocate resources efficiently to reduce energy usage.
Plant simulation refers to the process of simulating the operation and control of a large-scale facility by implementing and simulating various systems, processes, equipment, etc. of a real plant (facility) in a virtual environment through computer software. Typically, these simulations are used to proactively detect and resolve problems throughout the entire process, from the plant design phase to operation and maintenance. This can increase safety, efficiency, productivity, and improve a facility or process.
Plant simulation can be used in a variety of industries, including petrochemical plants, power plants, manufacturing, and air transportation. It can be used to predict and prepare for problems or costs that may arise in the field, as well as for training and scenario testing in real-world operations.
-
01
Process modeling and dynamic simulation
- The key to plant simulation is to accurately model the various processes within the plant and perform dynamic simulation based on them
- Simulate the behavior of a process over time, taking into account physical and chemical processes, control systems, sensor and actuator behavior, and more.
-
02
Control system simulation
- During plant operation, various control systems play a role in keeping the process stable and optimized. These control systems should also be incorporated in the simulation.
- PID controllers, logic controls, advanced control strategies, etc. are tested and optimized in simulation.
-
03
3D visualization and virtual site modeling
- Plant simulation provides 3D visualization with virtual site modeling. This allows the operator or engineer to visually see the components and processes within the plant.
- The virtual site model accurately reflects the layout and configuration of the actual facility and provides a visual understanding of the plant.
-
04
Real-time simulation and hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) testing
- Plant operations take place in a dynamic environment that changes in real time; therefore, real-time simulation enables testing under conditions similar to the actual operating environment of the plant.
- HIL testing validates the performance of the control system using the actual hardware in the plant and is integrated with the plant simulation to support testing on real hardware.
-
05
Application of big data and artificial intelligence (AI)
- Big data and AI technologies are used to collect and analyze large amounts of data generated by the plant, such as sensor data, control data, and maintenance records, to increase the efficiency of operations.
- This enhances capabilities such as predictive analytics, failure prevention, and optimization.
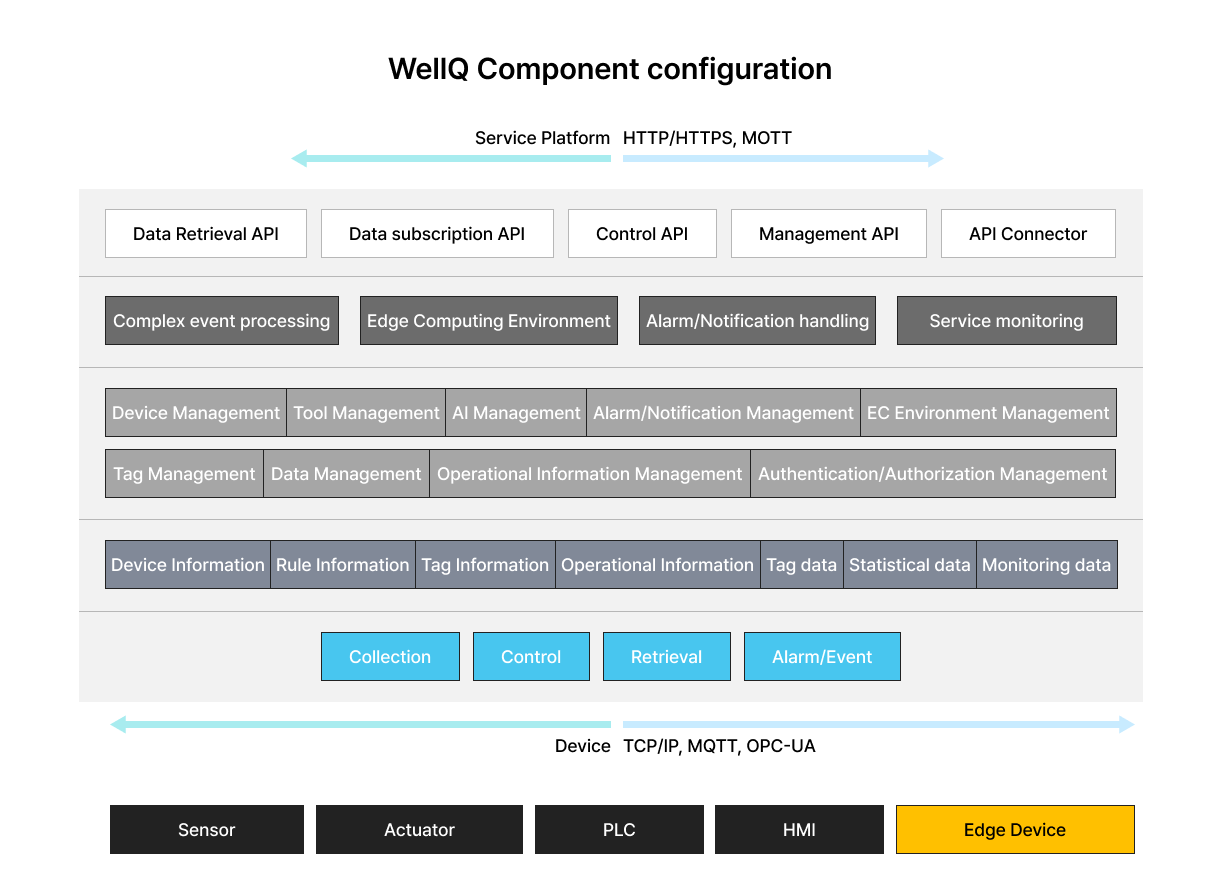
WellQ is an artificial intelligence IIoT edge computing platform that can run on a variety of edge hardware.
-
01
Data collection, storage, and transmission
- Supports OPC-UA and other PLC manufacturer-specific protocols
- Collect various sensor data through RS-232/485, BLE, LoRa, WiFi, etc.
- Hierarchical tagging and storage of large time series data
-
02
Equipment Control and Setup
- Provides MQTT real-time two-way control channel
- Ability to set parameters and recipes for equipment
-
03
Real-time Complex Event Processing (CEP)
- Processing and monitoring of real-time data
- Rule-based event processing
- Provides GUI for easy editing of complex rules
- Real-time notifications such as judgment and response to abnormal signs and sending SMS
-
04
Ensuring operational continuity and responding to failures
- Ensure continuity of facility operations by maintaining key operational information in case of disconnection from service platforms
- Synchronizing data between service platforms in case of failure recovery
-
05
AI + Edge Computing Environment
- Provide Kubernetes-based user application execution environment
- Provide API for integration with CEP
- Provide an environment to run trained ML and DL models